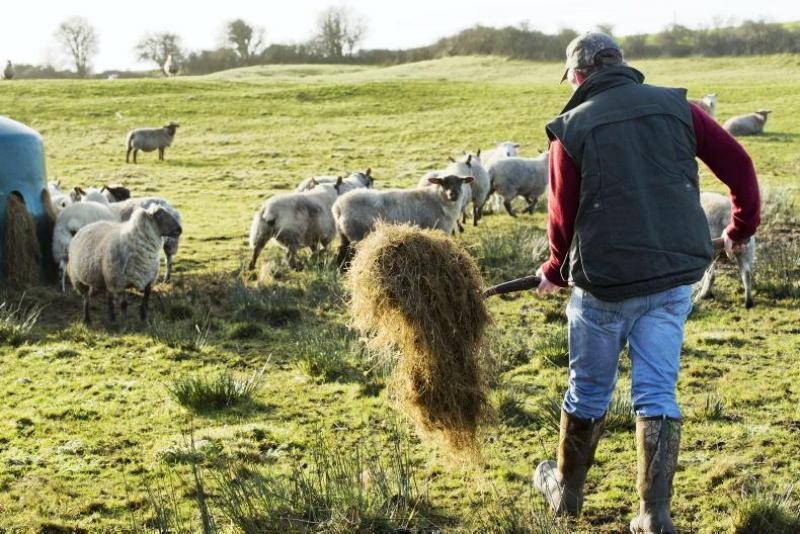

As of this year, the countries of the European Union have officially switched to the new principles of the Common Agricultural Policy. As part of the Common Agricultural Policy (CAP) reform, the EU will encourage and incentivize farmers who farm in an environmentally friendly and climate-friendly manner. In early January, the European Commission, the highest executive body of the European Union, published a list of agricultural practices that can receive support under the environmental CAP schemes. World of NAN decided to highlight some of the practices for which special payments are available and which, in the future, could be offered to our Kazakh farmers as well.
To begin with, we note that the Common Agricultural Policy (CAP) in the European Economic Community was introduced in 1992. It is designed not only to provide food to the population, but also to help increase incomes of farmers. Simply put, the CAP is a system of subsidies and support for agricultural programs in the EU.
Environmental programs, on the other hand, are a tool designed to encourage farmers who, along with production, aim to protect the environment while taking climate change into account.
Experts report that these programs will be voluntary rather than mandatory, but if they are waived, farmers will lose some of the payments they receive. That is, it is up to the farmer to decide to what extent she/he is ready to comply with the requirements for the transition to organic farming. At the same time, it should be emphasized that the EU will reimburse to farmers all the costs incurred in connection with the required tasks and even in some cases compensate the lost income.
Now the eco schemes will amount to 20 to 30% of the payments due to farmers. These payments will primarily be directed by the Eurasian Commission to farmers to fund agricultural practices based on climate, environmental or animal welfare issues.
"The future CAP will play a crucial role in the transition to a sustainable food production system and in the comprehensive support of European farmers. Environmental programs will make a significant contribution to this transition and to achieving the goals of the Green Deal," the EC said in a communiqué.
Thus, the Eurasian Commission intends to encourage farmers to engage in the most sustainable agriculture.
The list of agricultural practices that can be supported by green schemes is made on the basis of certain conditions. They must cover activities related to climate, environment, animal welfare and antimicrobial resistance.
Experts in the field of green economy have already identified potential areas in which EU farmers could develop their farms.
Conservation of water reserves
Payments for rehydration of moorlands and maintenance of the minimum groundwater level in winter could be envisaged in this direction. In addition, the EU proposes payments for the creation and wide use of grasslands.
Precision farming
Precision farming aimed at reducing the amount of fertilizers and pesticides. The EC is willing to finance farmers who farm with nutrient-enhanced soil fertility technologies.
Highly sustainable farming.
Farmers are ready to be rewarded for pasture-based livestock production. This will take into account the creation of good conditions for animals, without harming the environment.
Practices to reduce greenhouse gas emissions
Since beef and dairy products are the dominant sectors in agriculture, the EC's focus is on reducing methane emissions. To incentivize farmers, it is considering funding the purchase of feed additives by farmers to help reduce emissions from the enteric fermentation process and to improve manure management and storage.
Agroecology
There are a number of proposed farming practices that fall within the field of agroecology.
For tillage farmers, they include crop rotation with nitrogen-fixing crops.
Livestock and animal welfare
Eco programs originally focused on activities related to climate and the environment, but now a great deal of attention is being paid to animal protection as well. In this direction the Commission is ready to support the livestock breeders who use effective methods to increase the life span of farm animals and create favorable conditions for keeping livestock. One of the proposals is also to provide access to pastures and increase the grazing period for grazing animals.
Agroforestry
The Commission seeks to promote agroforestry. The EC provides payments to farmers for creating and maintaining landscape features, managing these features with a special cutting plan and creating pasture systems with high biodiversity, which include planting trees and shrubs on pastures.
Integrated pest management practices
The EC intends to reduce farmers' overall pesticide use and risk by 50% by 2030.
For the tillage sector, it has identified Integrated Pest Management (IPM) as a key way to achieve this goal.
Farmers in eco-programs are willing to provide subsidies for mechanical weed control, increased use of pest-resistant varieties and crop species.
To recall, eco-programs were piloted in 2014-2015 in European countries - England, Ireland and Spain. And already in 2019 at the Brussels conference, the EC reported on the positive results of the pilot projects.
The Commission now aims to bring 25% of all agricultural land in the EU under organic management by 2030. This means that the land will be used mainly for the production of organic food, while the area for the cultivation of fodder crops will be reduced. Kazakhstan's agrarians should take advantage of this by increasing the production of fodder crops for export, according to agribusiness analysts.











































Обсуждение