
When it comes to increasing wheat yields, it is impossible to bypass the topic of combating pests and all kinds of diseases. They are capable of negating all the efforts of farmers. It is known that epidemics of agricultural diseases, namely those that affect wheat, can occur every 3-4 years out of 10. If it develops moderately, annual crop losses amount to 10-15%, and in the period of epiphytoty or the spread of infectious diseases of plants these indicators can reach 40%. If agricultural land is contaminated with the same brown rust, then no matter what fertilizer is used, no matter what soil condition, a good harvest is unlikely to be achieved. Thus, for example, in the year of brown rust spread, the yield shortfall of spring wheat grain can reach 40-60%. This is what happened in the second half of the sixties in the North-Kazakhstan region. Then the harvesters of grain in the region lost 40-50% of the harvest because of this disease.
Septoria disease is an insidious enemy.
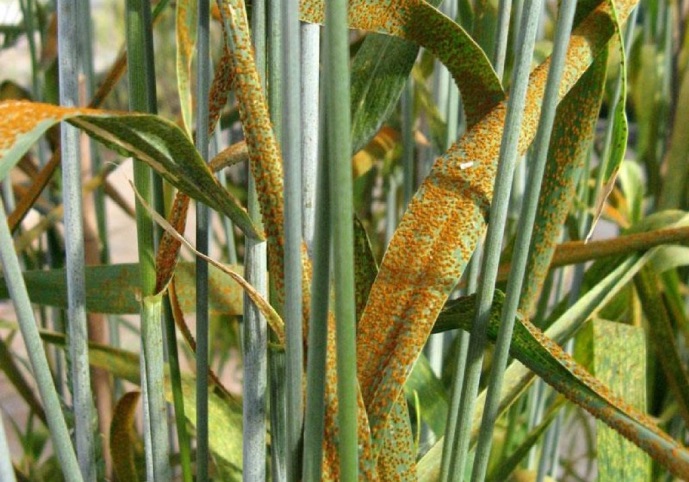
Another malicious enemy of crop growers is Septoria disease. This disease, caused by the so-called imperfect fungus Septoria tritici, affects mainly wheat, barley, rye and other grasses. Its main area is Western and Eastern Siberia, Altai and Primorsky regions of the Russian Federation. Septoria tritici can cause very serious harm to agrarians, so septoriosis is one of the economically significant diseases of agricultural crops. Thus, according to Russian experts, septoria is in the third place among the diseases of grains. Up to 40% of crops can be affected by this disease. Mainly, agricultural lands in Northern and Eastern Kazakhstan are exposed to this disease. And as is known - 78% of grain crops sowing is concentrated in Northern Kazakhstan. The plant affected by this fungus loses its leaves, its susceptibility to sunlight decreases, which as a result reduces productivity. In addition, there is underdevelopment of ears, and premature ripening of grains. An infected plant differs significantly from healthy plants in its slight growth, and the number of grains is reduced. When septoriosis is spread, grain losses can be as high as 30%.

Photo by agrofolio.by
Rains can also cause disease to spread, especially if they last for several days. In such conditions, at least 6 hours of leaf moistening and up to 48 hours of humidity are enough for maximum infestation. A key factor in the spread of Septoria tritici is the disregard for crop rotation and agronomic measures, which are designed to reduce the growth of infection in the soil, as well as insufficient weed control.
This indicates the influence of climate in the period of grain growth. If in southern regions of Kazakhstan winter wheat grains ripen at relatively low air humidity (30-40 %), septoriosis infestation does not occur. In northern regions of the republic grain ripens in conditions of high air humidity, in some years relative air humidity is 65-70 % and more, that influences septoriosis spreading.
Then how can crops be protected from this disease?
The main protective measures against septoriosis are optimal timing of sowing, balanced application of mineral fertilizers, fungicide treatment during the vegetation period, cultivation of resistant varieties. It is the use of herbicides that significantly increases the susceptibility of plants to septoriosis, as well as to rust diseases, powdery mildew. A special place in combatting septoriosis is given to agricultural practices, in particular, the cultivation of disease-resistant varieties. What was grown before the sowing of wheat is also important in controlling the level of septoriosis. Sowing of grains after oilseed or leguminous crops is recommended.
Rust strikes the farmland
In addition, three types of rust are among the most dangerous diseases of wheat in our country. These are brown or leaf rust, stem rust as well as yellow or stripe rust. In the north of our country, leaf rust is more widespread and causes more damage to spring wheat than stem rust.
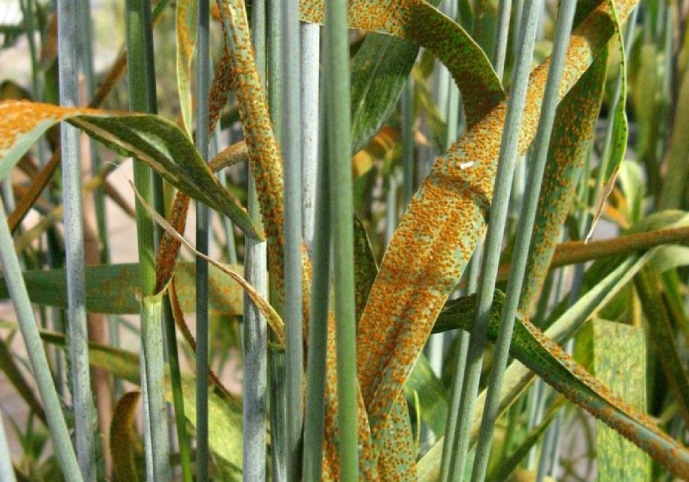

Photo by syngenta.kz. Brown (leaf) rust
Moreover, the infection of leaf and stem rust gets into the fields of the region with air flows from neighboring regions of Russia. The pathogens of this dangerous disease can also winterize, which leads to earlier spread of the disease on spring wheat. As with septoriosis, the main factor in the spread of rust is weather conditions. And while Septoria tritici develops at high air humidity, leaf and stem rust can spread in warm weather. Years of research have shown that septoria and brown rust can infect spring wheat simultaneously. Although which disease will dominate, depends on the weather conditions...














































Обсуждение